Comparison Between Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory.
Definition of Valence Bond Theory:
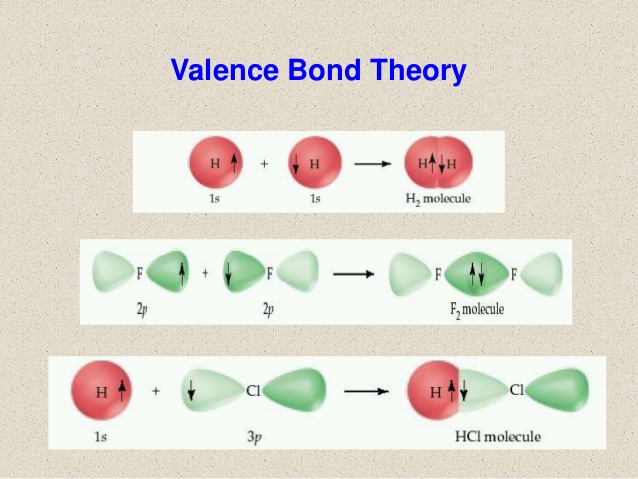 Valence Bond Theory considers that the overlapping atomic
orbitals of the participating atoms from a chemical bond. Valence bond theory views
bonds as weakly coupled orbitals.
Valence Bond Theory considers that the overlapping atomic
orbitals of the participating atoms from a chemical bond. Valence bond theory views
bonds as weakly coupled orbitals.
Definition of Molecular Orbital Theory:
Molecular orbital theory tells that electrons in a molecule
are not assigned to individual chemical bonds between atoms. but are treated as
moving under the influence of the atomic orbital nuclei in the whole molecule.
Comparison:
The valence bond theory defines the hybridization of
molecular orbitals where as the molecular theory doesn’t define anything about hybridization
of orbitals.
Valence bond theory can only be applied for diatomic
molecules whereas molecular orbital theory can be applied on polyatomic molecules.
In valence bond theory bonds are localized to two atoms and
not molecules while in molecular orbital theory, bonds are localized to both
two atoms and molecules.
In Valence bond theory there is no explanation of paramagnetic
character of oxygen where as in molecular orbital theory there is an elaborate
explanation of paramagnetic character of oxygen.
Valence bond theory has simplicity and convenience especially in terms of calculations whereas molecular orbital theory is somehow complex and hard in terms of calculation.
Author: Fardin Jaman Aronock
Date:20/9/2020




No comments